Diabetic Retinopathy: Diabetes is one of the fastest-growing health crises of our time, silently impacting millions of people worldwide. While many are aware of diabetes’ effects on the heart, kidneys, and nerves, its impact on vision is often overlooked. Among these vision-related complications, diabetic retinopathy stands out as the leading cause of vision loss in diabetics.
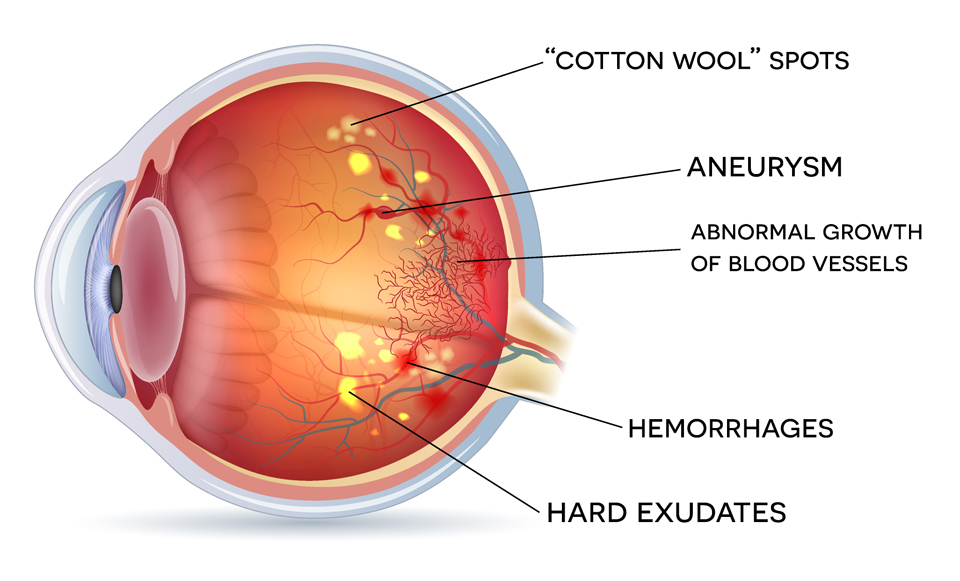
Diabetic retinopathy occurs when high blood sugar levels damage the tiny blood vessels in the retina, the light-sensitive tissue located at the back of the eye. Over time, this damage can impair the retina’s ability to send visual information to the brain, potentially resulting in blurred vision, floaters, scotomas (black spots), or even blindness if left untreated. This eye disease can develop silently during its early stages, making regular eye examinations crucial for early detection and management.
According to Dr. Aditya Kelkar, Director of NIO Super Specialty Hospital, “Early detection through regular eye checkup along with good sugar control can prevent serious complications and preserve vision of the affected person.” With diabetes cases rising rapidly in India, the number of diabetic retinopathy cases is also surging. This condition can affect all diabetic individuals, whether type 1 or type 2, and worsens the longer the person lives with poorly controlled diabetes.
What is Diabetic Retinopathy?
Diabetic retinopathy is a complication of diabetes caused by persistently high blood sugar levels damaging the retinal blood vessels. These vessels become weakened and leaky, leading to swelling or bleeding in the retina, and in advanced stages, abnormal blood vessel growth.
Why the Retina Is Crucial
The retina plays a pivotal role in vision by converting light into neural signals for the brain to interpret. Damage to this delicate tissue results in symptoms like blurred vision, dark spots, and eventual vision loss.
Who Is at Risk?
All individuals with diabetes are at risk, but the likelihood increases if:
- Blood sugar is poorly controlled
- The person has high blood pressure or high cholesterol
- Diabetes has been present for many years
Symptoms of Diabetic Retinopathy
Initially, diabetic retinopathy may not cause noticeable symptoms. As it progresses, symptoms may include:
- Dark floaters appearing in the visual field
- Blurred or distorted vision
- Scotomas (black or blank spots) in the vision
- Dull or weakened night vision
- Progressive loss of vision over time
It is typically bilateral, meaning it affects both eyes, and if left untreated, can lead to permanent blindness.
Stages of Diabetic Retinopathy
1. Non-Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy (NPDR)
This is the early stage where blood vessels in the retina start leaking, leading to swelling or macular edema. Vision may blur during this stage but often remains manageable with proper treatment and control of diabetes.
2. Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy (PDR)
An advanced stage where the eye grows abnormal, fragile blood vessels in an attempt to supply the damaged retina. These vessels can bleed into the vitreous, causing clouded vision, floaters, and, in severe cases, retinal detachment, which leads to irreversible vision loss.
Read about: Women Face 45% Higher Mortality Risk From Beta-Blockers After Heart Attack
How to Prevent Diabetic Retinopathy
1. Regular Eye Check-Ups
Annual comprehensive eye examinations can detect early signs of retinopathy before significant damage occurs.
2. Blood Sugar Control
Maintaining optimal blood glucose levels significantly reduces the risk of diabetic retinopathy development and progression.
3. Manage Blood Pressure and Cholesterol
Keeping blood pressure and cholesterol levels in check helps prevent further damage to retinal blood vessels.
4. Healthy Lifestyle Choices
- Balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains
- Regular physical activity
- Avoid smoking and limit alcohol intake
5. Early Medical Intervention
If diagnosed, treatments like laser therapy, intraocular injections, or vitrectomy can help prevent or slow the progression of vision loss.
Conclusion
Diabetic retinopathy is a silent yet serious complication of diabetes that can severely impact your vision and overall quality of life if left untreated. With early detection, strict blood sugar control, and healthy lifestyle choices, it is largely preventable.
As diabetes continues to rise across India, so does the incidence of diabetic retinopathy. Regular eye check-ups remain the most effective way to identify early signs and prevent permanent vision loss. Health experts stress that understanding the risks and symptoms of diabetic retinopathy empowers patients to take control of their health before it’s too late.
Don’t ignore subtle signs like floaters or blurred vision. Consult an eye specialist immediately to safeguard your sight and maintain your overall well-being.
Also read: Motilal Oswal Initiates Coverage on Bajaj Housing Finance: 3 Key Drivers to Watch
FAQs Diabetic Retinopathy
1. Can diabetic retinopathy cause blindness?
Yes, if left untreated, diabetic retinopathy can lead to permanent vision loss or blindness due to retinal detachment or severe macular edema. Early detection and treatment are key to preserving vision.
2. How often should a diabetic get their eyes checked?
It is recommended that all diabetic patients undergo a comprehensive eye exam at least once a year. More frequent check-ups may be necessary if there are signs of retinopathy or other complications.
3. Is diabetic retinopathy reversible?
While early-stage diabetic retinopathy can be managed and progression slowed with blood sugar control and lifestyle changes, advanced stages may require medical interventions like laser therapy or surgery. Complete reversal is not always possible, which makes early detection crucial.
4. What are the treatment options for diabetic retinopathy?
Treatments include laser photocoagulation to seal leaking vessels, anti-VEGF injections to reduce abnormal vessel growth, and vitrectomy surgery in severe cases. These interventions help slow or prevent vision loss.
5. Can a healthy lifestyle prevent diabetic retinopathy?
Yes, maintaining a balanced diet, regular exercise, controlled blood sugar levels, and regular eye exams are essential preventive measures. A healthy lifestyle plays a vital role in reducing the risk of developing diabetic retinopathy and its complications.

yqf048