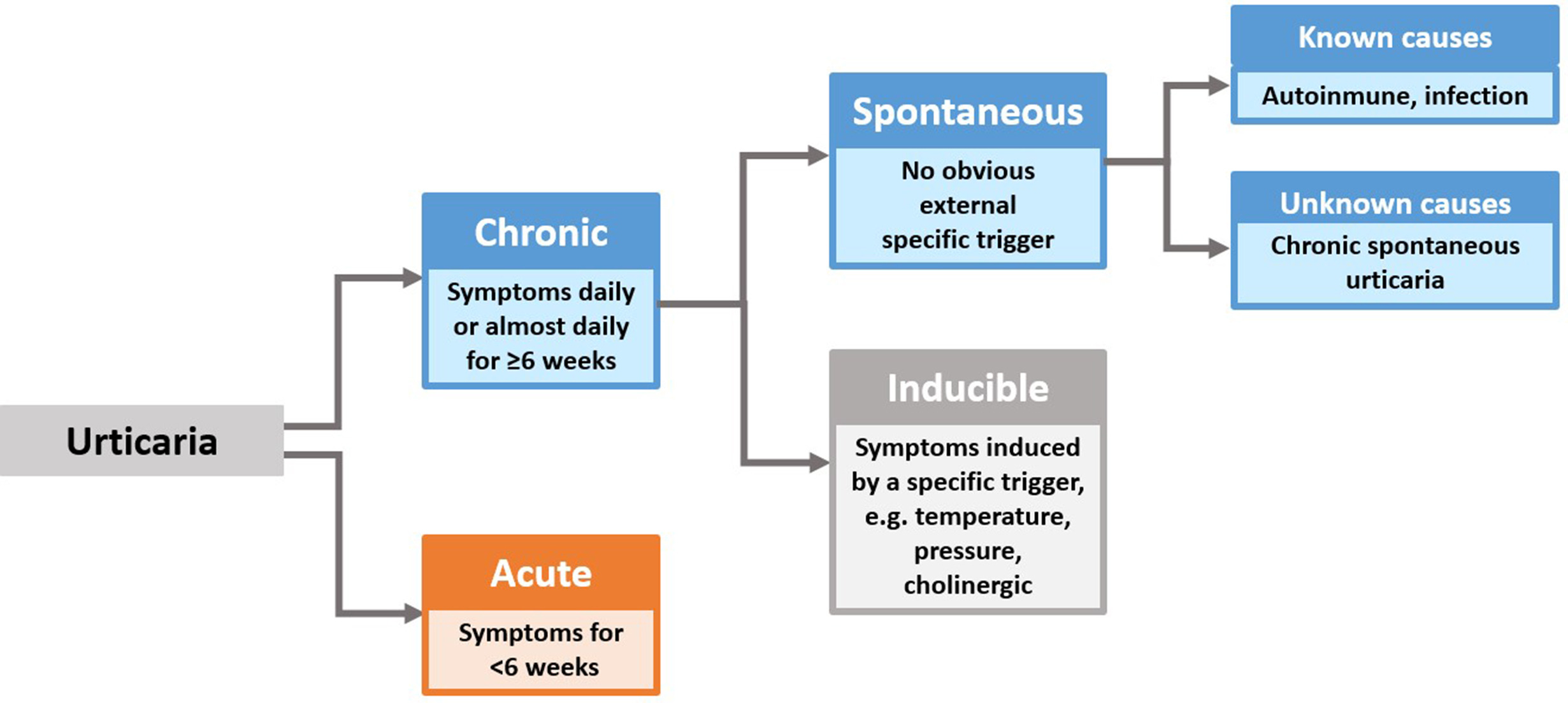
Patient Preferences in Chronic Urticaria Treatments: Chronic urticaria (CU), characterized by persistent hives, itching, and swelling, affects thousands of patients worldwide, significantly impacting quality of life. While clinical efficacy remains central to treatment selection, emerging research underscores that understanding what patients value most is crucial to delivering care that aligns with their needs. A recent systematic review, covering 18 studies and over 28,000 participants, provides compelling insights into patient and caregiver preferences in chronic urticaria treatments, highlighting factors beyond mere clinical outcomes.
For individuals living with CU, daily symptoms can be physically uncomfortable and emotionally taxing. The unpredictability of flare-ups, coupled with itching, swelling, and visible hives, often disrupts sleep, work, and social life. Against this backdrop, treatment decisions are not solely guided by effectiveness; speed of relief, safety, convenience, and long-term control emerge as decisive factors. Understanding these priorities allows healthcare providers to tailor care in ways that enhance adherence, satisfaction, and overall quality of life.
The review’s findings illustrate that patient-centered care goes beyond prescribing effective medications. Patients consistently seek treatments that deliver rapid symptom relief, minimize side effects, and integrate seamlessly into daily routines. By considering these preferences, clinicians can bridge the gap between clinical goals and patient experiences, ensuring that management strategies for chronic urticaria truly address what matters most to those affected.
Rapid Relief and Safety Are Top Priorities
Among patients with chronic urticaria, speed of symptom relief is a critical determinant in treatment choice. According to the review, participants consistently valued medications capable of providing noticeable improvement within two weeks, reflecting the urgency of managing itching, swelling, and hives. Rapid-acting treatments reduce discomfort quickly, enabling patients to regain control over daily activities and emotional well-being.
However, efficacy alone is not sufficient. Safety and tolerability are equally important. Patients preferred options with milder adverse effects, such as minor injection site reactions, over treatments associated with serious risks, including kidney impairment. The review emphasizes the delicate balance between rapid symptom relief and long-term safety, which patients weigh carefully when choosing between treatments.
Read about: Rising Antibiotic Resistance: Routine Infections Return to the Danger Zone
Convenience and Ease of Use
Beyond symptom control, patients and caregivers prioritize treatment convenience. Oral and topical medications are generally preferred over injections or intravenous infusions, which are often viewed as disruptive or burdensome. This preference reflects a broader desire for autonomy, minimal disruption to daily life, and ease of adherence.
Convenient treatments allow patients to maintain routines without frequent hospital visits, complex administration, or logistical challenges. For caregivers, manageable therapies reduce caregiving burden, making compliance and monitoring easier while improving overall patient satisfaction.
Implications for Clinical Practice
The review highlights a clear takeaway for clinicians: treatment decisions should incorporate patient preferences alongside clinical efficacy. By prioritizing rapid relief, sustained control, safety, and ease of use, healthcare professionals can better align care with what patients truly value.
Integrating these considerations into shared decision-making enhances treatment adherence, reduces frustration, and promotes a more positive patient experience. Ultimately, patient-centered approaches ensure that chronic urticaria management is not only medically effective but also aligned with individual lifestyles and priorities.
Conclusion
Patient preferences are pivotal in managing chronic urticaria. Rapid symptom relief, treatment safety, convenience, and sustained control are consistently highlighted as top priorities by patients and caregivers.
Treatments that address these factors foster greater adherence, improved satisfaction, and enhanced quality of life, demonstrating that patient values should guide clinical decisions alongside clinical efficacy.
Healthcare providers can leverage these insights to implement personalized care strategies, ensuring treatment plans reflect both medical and patient-centered goals.
By focusing on what truly matters to patients, clinicians can transform chronic urticaria care from a purely clinical intervention into a holistic, patient-focused experience.
Also read: Patient Preferences in Chronic Urticaria Treatments
FAQs of Patient Preferences in Chronic Urticaria Treatments
1. What are the most important factors for patients when choosing chronic urticaria treatments?
Patients prioritize rapid symptom relief, long-term control of hives, itching, and swelling, minimal side effects, and ease of use. Convenience and treatment safety are as crucial as effectiveness.
2. How quickly do patients expect relief from urticaria treatments?
According to the review, patients prefer medications that provide noticeable improvement within two weeks, emphasizing the need for rapid symptom management to reduce daily discomfort.
3. Why is treatment convenience important in chronic urticaria?
Oral and topical treatments are favored because they are easier to use and less disruptive to daily routines. Treatments requiring injections or infusions may burden patients and caregivers, affecting adherence and overall satisfaction.
4. How do safety concerns influence treatment decisions?
Patients favor therapies with milder side effects, such as minor injection site reactions, and generally avoid treatments linked to serious risks like organ impairment. Safety is weighed alongside speed of relief in choosing therapy.
5. How can clinicians incorporate patient preferences into chronic urticaria care?
Healthcare providers should engage in shared decision-making, discussing treatment speed, convenience, safety, and long-term control with patients. Aligning treatment strategies with these priorities improves adherence, satisfaction, and quality of life.











2 thoughts on “Patient Preferences in Chronic Urticaria Treatments: What Truly Matters”