US Prostate Cancer Rates: Prostate cancer, long considered one of the most common cancers affecting men, is back in the spotlight as new data reveals a disturbing trend in the United States. According to a recent report from the American Cancer Society, prostate cancer cases have surged sharply over the past decade, reversing years of steady decline. What makes this spike even more concerning is the fact that many of these cases involve advanced-stage prostate cancer, which is more aggressive and harder to treat successfully.
Experts believe that multiple factors are driving this surge. One major reason may be linked to reduced prostate-specific antigen (PSA) testing, after the US Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) discouraged routine screening in the early 2010s. This shift likely led to fewer men being diagnosed early, allowing cancers to progress undetected until reaching advanced stages. Beyond screening, lifestyle changes, environmental factors, and dietary patterns may also be contributing to the sudden rise.
This increase is particularly alarming because prostate cancer often develops silently, with little to no symptoms in its early stages. Many men only discover the disease once it has spread beyond the prostate gland, making treatment more complex. To better understand this growing health challenge, let’s break down what prostate cancer is, its early symptoms, risk factors, and most importantly, the steps men can take to lower their risk and catch the disease at an earlier, more treatable stage.
What is Prostate Cancer?
The prostate is a walnut-sized gland located below the bladder and in front of the rectum. Its main function is to produce seminal fluid that nourishes and transports sperm. Prostate cancer occurs when cells in the prostate begin to grow uncontrollably. While some prostate cancers grow slowly and may not pose an immediate threat, aggressive forms can spread quickly to the bones, lymph nodes, and other vital organs.
According to the American Cancer Society, about 1 in 8 men will be diagnosed with prostate cancer in their lifetime. The risk increases with age, but family history, race, genetics, and lifestyle factors also significantly influence vulnerability.
Why Are US Prostate Cancer Rates Rising?
1. Changes in Screening Practices
The USPSTF’s 2012 recommendation against routine PSA screening was intended to reduce unnecessary treatments, but it also resulted in fewer early diagnoses. Many cancers that might have been caught early were left undetected until they became more advanced.
2. Environmental and Lifestyle Factors
Changes in dietary habits, rising obesity rates, and environmental exposures may be playing a role. Certain pesticides and chemicals in farming communities have also been linked to higher risk.
3. Increased Awareness and Reporting
In some cases, improved diagnostic tools and increased awareness may be driving up reported cases, though experts emphasize that the trend in advanced cancers is what makes this rise particularly worrisome.
Read about: Fast Food Addiction: How Convenience Eating Is Reshaping Indian Health
Early Signs and Symptoms of Prostate Cancer
One of the biggest challenges with prostate cancer is its silent progression. Early-stage prostate cancer often has no clear symptoms, but as the disease advances, warning signs may include:
- Frequent urination, especially at night
- Difficulty starting or stopping urination
- Weak or interrupted urine flow
- Blood in urine or semen
- Erectile dysfunction or painful ejaculation
- Pelvic discomfort
In advanced cases, cancer that spreads to bones or nerves can cause back pain, bone pain, unexplained weight loss, fatigue, or spinal issues. Since many of these symptoms can also be linked to benign conditions like enlarged prostate or infections, it is crucial to seek medical evaluation rather than self-diagnosing.
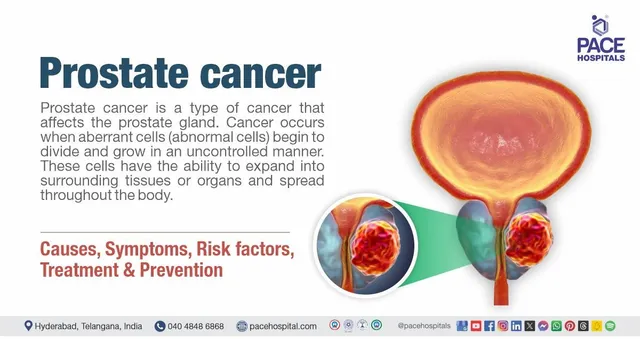
Who is Most at Risk?
Certain groups face a higher risk of prostate cancer. Key factors include:
Age
- Most diagnoses occur in men over 65 years old, with the average age being 68.
Family History & Genetics
- Having a father or brother with prostate cancer doubles the risk.
- Genetic mutations such as BRCA2 and HOXB13 can increase susceptibility.
Race & Ethnicity
- Black men have significantly higher incidence rates and often face more aggressive forms of the disease.
Lifestyle Factors
- Obesity, high cholesterol, and even height are linked to increased risk.
- Regular physical activity, especially vigorous exercise, may reduce risk.
Dietary Habits
- Diets rich in red meat, high-fat foods, and processed meals may raise risk.
- Consuming fish, soy, cruciferous vegetables (like broccoli), and tomatoes (rich in lycopene) may lower risk.
Prevention Tips: Reducing Your Risk of Prostate Cancer
While not all cases can be prevented, men can take several steps to lower their risk and improve overall health outcomes:
- Regular Screening
- Discuss PSA testing with your doctor, especially if you have risk factors. Early detection remains the strongest weapon against aggressive prostate cancer.
- Healthy Diet
- Increase intake of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein.
- Reduce processed foods, excessive dairy, and high-fat red meats.
- Exercise and Weight Management
- Aim for 150 minutes of moderate exercise per week.
- Maintaining a healthy weight helps reduce cancer progression risks.
- Limit Alcohol and Quit Smoking
- Both habits are linked to poor overall health and may increase cancer risk.
- Know Your Family History
- If prostate cancer runs in your family, consider earlier and more frequent screenings.
Also read: Radical Audi TT Concept 2025 – Retro-Inspired Sports Coupé Previewed Ahead of Munich Motor Show
Conclusion
The recent rise in US prostate cancer rates is a reminder that men’s health cannot be ignored. After years of declining numbers, the sharp increase—especially in advanced cases—signals the need for renewed focus on early detection, healthy living, and targeted prevention strategies.
For many men, the disease remains invisible until it reaches a dangerous stage, which is why understanding the early warning signs and risk factors is so important. Knowledge empowers men to take control of their health through proactive screenings and lifestyle changes.
The good news is that while certain risk factors like age and genetics cannot be controlled, modifiable habits such as diet, exercise, and regular medical checkups can make a significant difference. By embracing healthier choices and having open discussions with healthcare providers, men can lower their risks and improve outcomes.
Ultimately, reversing this alarming trend requires a multi-pronged approach—individual responsibility, improved screening policies, and stronger community awareness. With the right strategies in place, prostate cancer can be detected earlier, treated more effectively, and prevented in many cases.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Why are prostate cancer rates rising again in the US?
The surge is linked to reduced PSA screening after the USPSTF discouraged routine tests, which allowed more cancers to remain undetected until advanced stages. Lifestyle factors, environment, and better reporting may also contribute.
2. At what age should men start screening for prostate cancer?
Most men should begin discussing screening around age 50, but those at higher risk—such as Black men or those with a strong family history—should consider starting at 40–45. Screening usually involves a PSA blood test and sometimes a digital rectal exam.
3. What are the early symptoms of prostate cancer?
Prostate cancer often has no symptoms in its early stages. Later signs may include frequent urination, weak urine flow, blood in urine or semen, erectile dysfunction, and pelvic discomfort. Advanced cases may cause back or bone pain and unexplained weight loss.
4. How can lifestyle changes reduce prostate cancer risk?
Adopting a balanced diet rich in vegetables, fish, and whole grains, exercising regularly, maintaining a healthy weight, and avoiding smoking or excessive alcohol can all help reduce risk. While not foolproof, these measures improve overall health and lower chances of aggressive disease.
5. Is prostate cancer always deadly?
No. Many prostate cancers grow slowly and may not require aggressive treatment. However, aggressive and advanced forms can spread quickly and become life-threatening. That’s why early detection and regular checkups are critical for improving survival outcomes.











